The official currency of Jamaica is the Jamaican dollar (JMD), which has been in circulation since 1969. The JMD is abbreviated as J$, and it is divided into 100 cents, although cent denominations are no longer in use as of 2018.
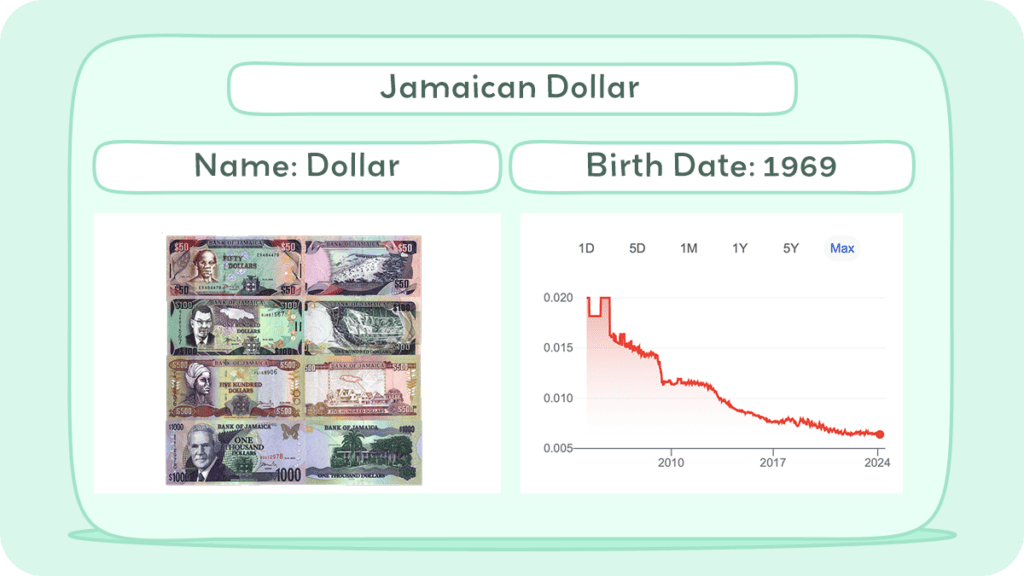
The Jamaican currency is managed by the Bank of Jamaica, which is responsible for issuing banknotes and coins. The banknotes come in denominations of JMD 50, 100, 500, 1000, and 5000, while the coins are available in denominations of JMD 1, 5, 10, and 20.
This article explores the history and unique characteristics of the Jamaican dollar, offering insights into its origins, design, cultural significance, and potential future in the global financial landscape.
Historical Journey of Jamaican Currency
Jamaican currency has been through many changes throughout history. Before the arrival of the Spaniards in the early 16th century, there was little use for a regular currency as trade was conducted by barter.
However, after the arrival of the Spaniards, gold was introduced as a means of trade. The Taino Indians, Jamaica’s first inhabitants, used gold for decorative purposes, but the Spaniards used it for trade.
In 1660, the British took control of Jamaica and introduced the British pound as the official currency. The Spanish dollar was also in circulation, but it was gradually phased out.
In 1839, the Planters Bank was established and issued banknotes, which were used alongside the British pound. This led to confusion, and in 1840, the British pound was made the sole legal tender in Jamaica.
In 1869, the Jamaican pound was introduced, which was equivalent in value to the British pound. The Jamaican pound was divided into 20 shillings, and each shilling was divided into 12 pence.
In 1969, the Jamaican dollar was introduced to replace the Jamaican pound. The Jamaican dollar was initially equivalent in value to the US dollar, but its value has fluctuated over the years.
Today, the Jamaican dollar is the official currency of Jamaica and is divided into 100 cents. While cent denominations are no longer in use, goods and services may still be priced in cents. Cash transactions are rounded to the nearest dollar.
Overall, the historical journey of Jamaican currency has been marked by changes in currency and fluctuations in value. Today, the Jamaican dollar remains an important part of the country’s economy and daily life.
History of Coins
In 1969, Jamaica introduced its currency with coins in denominations of 1, 5, 10, 20, and 25 cents, mirroring the sizes, shapes, and compositions of previous coins except for a smaller bronze 1 cent.
The 1-cent coin transitioned to a twelve-sided, aluminum design in 1975, and in 1976, decagonal 50-cent coins were introduced, ceasing production in 1989 along with the 20-cent coins.
The year 1990 saw the introduction of nickel-brass 1 dollar coins, replacing the corresponding banknote. In 1991, 5, 10, and 25-cent coins were made of nickel-plated steel with new shapes and sizes, including a seven-sided 25-cent coin.
By 1994, Jamaica had introduced a round nickel-plated steel 5-dollar coin, a smaller seven-sided 1-dollar coin, and discontinued the 5-cent coin. Smaller, round copper-plated steel 10 and 25-cent coins appeared in 1995, with all non-current coins demonetized in January 1997.
A scalloped nickel-plated steel 10-dollar coin in 1999 and a bimetallic 20-dollar coin in 2000 replaced their banknote counterparts.
Currently, circulating coins include 1 dollar (seven-sided), 5 dollars (round), 10 dollars (scalloped or round), and 20 dollars (bimetallic round), featuring prominent Jamaican figures on the reverse.
Demonetized coins include the 1 cent (dodecagon), 5 cents (round), 10 cents (round, then round copper-plated steel), 20 cents (round), 25 cents (round, then round copper-plated steel), and 50 cents (decagon), each with unique reverse designs ranging from natural imagery to historical figures, all demonetized by 15 February 2018.
History of Bills
Jamaica introduced its currency in 1969 with banknotes in denominations including 50 cents, $1, $2, and $10. Over time, more denominations were added such as the $5 note in 1970, $20 in 1976, $100 in 1986, and $50 in 1988.
The $2 and $1 notes were eventually phased out in favor of coins. By 1994, $5 notes were replaced with coins, and new higher denominations like $500 notes were introduced. In subsequent years, $10 and $20 notes were also replaced by coins, and $1000 notes were added to circulation.
Currently, Jamaican banknotes include $50, $100, $500, and $1000 denominations, each featuring prominent national figures and landmarks. In 2009, a $5000 bill was introduced, bearing the portrait of former Prime Minister Hugh Lawson Shearer.
Additionally, a $50 commemorative note was issued in 2010 to celebrate the Bank of Jamaica’s 50th anniversary, and in 2012, a new family of banknotes was released to commemorate Jamaica’s Golden Jubilee, featuring the “Jamaica 50” logo.
Jamaican banknotes are primarily printed on cotton and enhanced substrates for durability, with some notes being printed on a “hybrid” material for added protection against wear and moisture.
In 2022, a new series of banknotes was introduced, including a new $2000 denomination, to commemorate Jamaica’s 60th anniversary.
The Jamaican dollar was historically used by the Cayman Islands and Turks and Caicos Islands until they adopted their own currencies in the early 1970s.
When adopting its decimal currency, Jamaica chose to use the half pound unit, naming its currency the dollar, aligning its value more closely with the US dollar rather than the British pound.
Inflation and Buying Power of Jamaican Currency
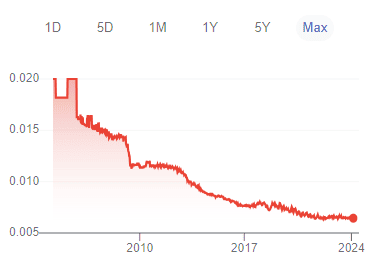
Jamaica has experienced high inflation rates in the past, which have affected the buying power of the Jamaican currency. According to the Bank of Jamaica (BOJ), the country’s central bank, its primary objective is to ensure price stability in the economy.
One way they do this is by implementing inflation targeting, which aims to keep inflation within a specific target range. As of 2024, Jamaica’s inflation rate is relatively stable, hovering around 4-6% annually.
Despite the efforts to keep inflation in check, the buying power of the Jamaican currency has still been affected. This is because inflation affects the prices of goods and services, making them more expensive over time.
For example, if you purchased a loaf of bread for JMD 100 in 2020, you would need to pay around JMD 106 in 2024 due to inflation.
To combat the effects of inflation on the buying power of the Jamaican currency, the BOJ has implemented various measures. One such measure is the use of interest rates.
By raising interest rates, the BOJ can encourage people to save more money, which reduces the amount of money in circulation. This, in turn, can help to reduce inflation and maintain the buying power of the Jamaican currency.
Another measure is the use of monetary policy, which involves controlling the money supply in the economy. By adjusting the money supply, the BOJ can influence inflation rates and maintain the buying power of the Jamaican currency.
Overall, the BOJ is committed to ensuring price stability and maintaining the buying power of the Jamaican currency. While inflation can affect the buying power of the Jamaican currency, the measures implemented by the BOJ aim to keep inflation within a specific target range and maintain the value of the Jamaican currency.
Jamaican Dollar
The Jamaican banknotes in circulation feature prominent national figures on the front and significant cultural or historical sites on the back. Here’s a summary of each denomination:
$50
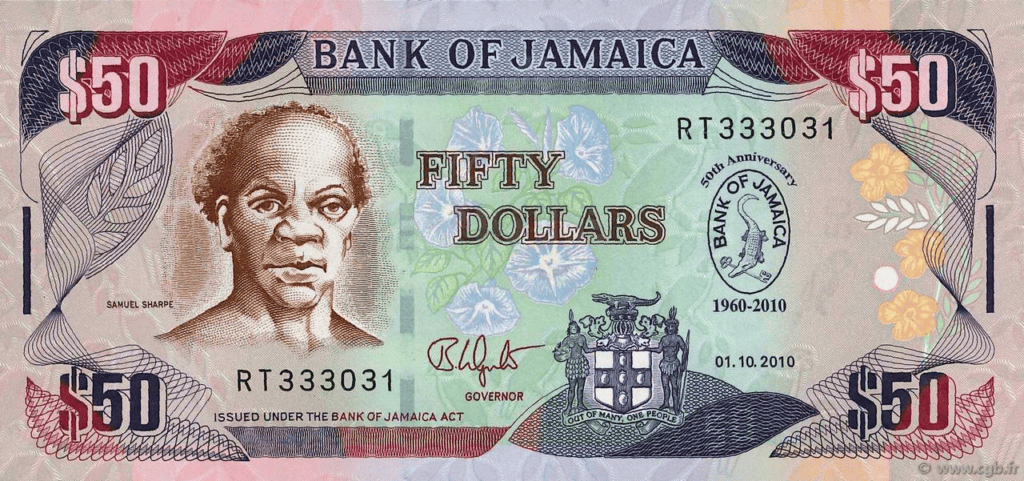
$50 Note: The front features The Right Excellent Samuel Sharpe, a national hero recognized for his role in the fight for emancipation. The back showcases Doctor’s Cave Beach in Montego Bay, a popular and beautiful tourist destination.
$100

$100 Note: The front depicts Sir Donald Sangster, a former Prime Minister, while the back displays Dunn’s River Falls, one of Jamaica’s most famous and stunning natural attractions.
$500

$500 Note: The front honors The Right Excellent Nanny of the Maroons, a national hero known for her leadership during the Maroon wars against the British in the 18th century. The back features an Old Map of Jamaica highlighting Port Royal, a historical city known for its pirate history.
$1000
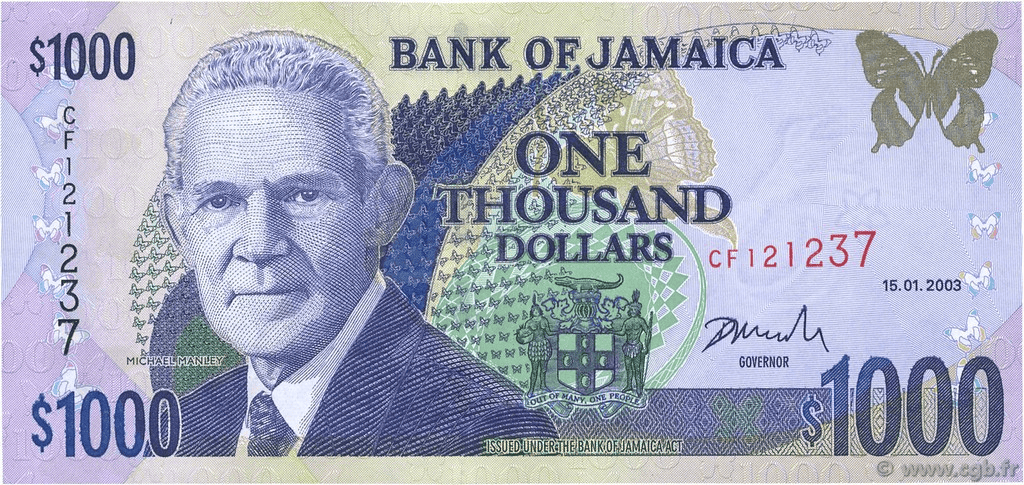
$1000 Note: The front showcases The Honourable Michael Norman Manley, a former Prime Minister noted for his contributions to social reform and equality. The back has Jamaica House, the official residence of the Prime Minister.
These banknotes not only serve as legal tender but also celebrate Jamaica’s rich history, culture, and contributions of key figures to the nation’s development.
Currency Usage in Jamaica
If you’re planning a trip to Jamaica, you might be wondering about the currency usage in the country. The official currency of Jamaica is the Jamaican dollar (JMD), which is abbreviated as “J$”. However, USD is widely accepted in Jamaica, especially in tourist areas.
Is USD accepted in Jamaica?
Yes, USD is widely accepted in Jamaica, but it’s always a good idea to have some Jamaican dollars on hand for purchases outside of tourist areas.
When using USD, it’s important to note that the exchange rate may not be in your favor, so it’s best to check the current exchange rate before making any purchases.
When exchanging currency, it’s recommended to do so at a bank or authorized exchange bureau to ensure you’re getting a fair exchange rate. It’s also important to note that some businesses may only accept cash, so it’s a good idea to have some cash on hand in both USD and JMD.
Exchanging Currency in Jamaica
Where can I exchange Jamaican currency?
When traveling to Jamaica, it is important to know where you can exchange your currency. Jamaican dollars (JMD) are the official currency of Jamaica, and you will need to exchange your foreign currency for JMD to make purchases.
You can exchange currency at banks, exchange bureaus, hotels, and airports. Banks and exchange bureaus typically offer the best exchange rates but may charge a commission or fee for the service. Hotels and airports may offer convenience, but they often have higher exchange rates and fees.
What to know before exchanging currency in Jamaica
Before exchanging your currency, it is important to know the current exchange rate. You can check the current exchange rate online or at a local bank or exchange bureau. Keep in mind that exchange rates can fluctuate daily, so it is important to check the rate before exchanging your currency.
When exchanging currency, make sure to count your money before leaving the counter. Also, be aware of any fees or commissions that may be charged for the service. Some places may have hidden fees or charge a higher commission than others, so it is important to compare rates before exchanging your currency.
It is also important to note that some places may not accept certain currencies for exchange. It is best to exchange your currency for Jamaican dollars before arriving in Jamaica to avoid any issues with acceptance.
Choosing Between USD and Jamaican Currency
When traveling to Jamaica, you may be wondering whether to use US dollars or Jamaican currency. Here are some factors to consider:
Exchange Rate
The exchange rate between USD and Jamaican currency fluctuates, so it’s important to check the current rate before making any transactions. Remember that you may get a different rate depending on where you exchange your currency.
Convenience
While some businesses in Jamaica accept USD, it’s generally more convenient to use Jamaican currency. Many smaller shops and restaurants may not accept USD, and you may receive a change in Jamaican currency regardless. Additionally, using Jamaican currency can help you avoid confusion and potential scams.
Fees
When exchanging currency, be aware of any fees involved. Some exchange bureaus and banks may charge a commission or a flat fee for exchanging currency.
Additionally, if you withdraw cash from an ATM, your bank may charge a foreign transaction fee. Be sure to check with your bank and compare rates and fees before making any transactions.
Tips
Here are some tips for managing your currency while in Jamaica:
- Carry small bills and coins for smaller transactions.
- Avoid exchanging currency at the airport, as rates may be less favorable.
- Consider using a credit card for larger transactions, as many offer favorable exchange rates and may waive foreign transaction fees.
- Be aware of potential scams, such as vendors giving incorrect change or offering to exchange currency at unfavorable rates.
Considering these factors, you can make an informed decision about whether to use USD or Jamaican currency during your trip to Jamaica.
Cost of Living in Jamaica
If you are planning to move to Jamaica, it’s important to have an idea of the cost of living. The cost of living in Jamaica is generally lower than in the United States and the United Kingdom.
According to Numbeo, the cost of living index in Jamaica is 50.55, which is lower than the UK’s 69.08 and the USA’s 76.86. This means that on average, it is cheaper to live in Jamaica than in the UK or USA.
The cost of living in Jamaica varies depending on several factors, including location, lifestyle, and accommodation.
If you are planning to rent a house or apartment in Jamaica, you can expect to pay around 69.6% less than in the United States. However, if you are planning to purchase a property, the cost may be higher.
Utilities in Jamaica are relatively expensive. According to International Living, electricity rates in Jamaica cost US$0.307 per kWh for households. Other recurring monthly expenses to consider include water, internet, cable, and maintenance. Most of these can be paid online.
Food prices in Jamaica can vary depending on whether you choose to eat out or cook at home. If you want to save money, you can cook at home and buy groceries from local markets. According to Expatistan, a single person’s estimated monthly costs for food are around $500 USD.
Overall, the cost of living in Jamaica is relatively affordable compared to other countries. However, it’s important to keep in mind that costs can vary depending on your lifestyle choices and location.
Don’t Get Scammed Tips
If you are traveling to Jamaica, it is important to be aware of the currency and exchange rates to avoid getting scammed. Here are some tips to help you navigate Jamaican currency and avoid scams:
1. Know the exchange rate
Before you travel to Jamaica, research the current exchange rate for your home currency to Jamaican dollars (JMD). This will help you avoid being taken advantage of by merchants who may try to give you less than what your money is worth.
2. Use ATMs
Using ATMs is a safe and convenient way to get cash in Jamaica. However, make sure to use ATMs located in well-lit, public areas to avoid being robbed. Additionally, check with your bank to see if they have partnerships with banks in Jamaica to avoid foreign transaction fees.
3. Be cautious with street vendors
Street vendors in Jamaica are known for their persistence in trying to sell their products. While some of them may offer good deals, others may try to scam tourists by giving them fake currency or short-changing them. Always count your change before leaving and be wary of vendors who only accept large bills.
4. Avoid currency exchange on the street
Currency exchange on the street may seem like a convenient option, but it can be risky. Scammers may offer to exchange your currency at a higher rate than the banks, only to give you counterfeit bills or less money than you are owed. Stick to reputable exchange offices or banks to ensure that you get a fair exchange rate.
By following these tips, you can enjoy your trip to Jamaica without worrying about getting scammed with currency.